Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitano, Akihiro; Takegoshi, Atsushi*; Hazama, Taira
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(7), p.992 - 1008, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:60.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)A feedback reactivity measurement technique was developed based on a reactivity model featuring components that depend on the reactivity coefficients, denoted as reactor power (K ) and reactor vessel inlet temperature (K
) and reactor vessel inlet temperature (K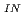 ). This technique was applied to the feedback reactivity experiment conducted in the Monju system start-up test in May 2010. A thorough evaluation considering all possible biases and uncertainties revealed that the reactivity coefficients can be evaluated with a measurement uncertainty smaller than 3%. The evaluated reactivity coefficients were simulated considering the temperature distribution in the core. The C/E value of K
). This technique was applied to the feedback reactivity experiment conducted in the Monju system start-up test in May 2010. A thorough evaluation considering all possible biases and uncertainties revealed that the reactivity coefficients can be evaluated with a measurement uncertainty smaller than 3%. The evaluated reactivity coefficients were simulated considering the temperature distribution in the core. The C/E value of K showed good agreement between calculated and measured values within the established uncertainty, and the value of K
showed good agreement between calculated and measured values within the established uncertainty, and the value of K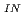 was consistent with that reported in a previous isothermal temperature coefficient experiment. The measured and calculated fuel subassembly outlet temperatures also agreed well within 0.2
was consistent with that reported in a previous isothermal temperature coefficient experiment. The measured and calculated fuel subassembly outlet temperatures also agreed well within 0.2 C.
C.
JNC TN4400 2000-002, 33 Pages, 2000/06
An on-site plant analyzer can provide analysis support in evaluating plant dynamic characteristics when unplanned events occur in a nuclear power station. The plant analyzer contains a plant-dynamics analysis code, which efficiently and quickly analyzes the plant dynamic characteristics. Elements being developed for the on-site plant analyzer include utilities to build plant models for performing analyses and to retrieve plant operation data. The addition of these elements to the analysis code supports the plant-dynamics analysis works in MONJU, in particular, to assist the analyses of start up tests. The system contains the FBR plant-dynamics analysis code "Super-COPD", which is based on the "COPD" code that was used in the safety licensing of MONJU. One feature of the system is that all operations, e.g., assembling plant models for analysis, are prepared using a GUI (Graphical user Interface). In addition to this feature, the system is able to retrieve directly on- and off-line plant data from MIDAS, the Monju Integrated Data Acquisition System. These plant data are used to supply time-dependent boundary conditions for the plant analysis models. For this report, two case studies were performed. First, the analysis result of a turbine trip test at 40% power operation using the full plant model is described. For the second, performance of the IHX model was evaluated using retrieved plant data for boundary conditions. With the development of this system, improvement in the efficiency of analyses of MONJU start-up tests is expected.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Sakai, Takaaki; ; Yamaguchi, Akira; Nishi, Yoshihisa*; Ueda, Nobuyuki*; *
JNC TN9400 2000-077, 223 Pages, 1999/05
The feasibility study (Phase l) is being carried out at JNC to build up new design concepts of practical fast reactors (FRs) from the viewpoint of economy, safety, effective use of resources, reduction of environmental burden and non-proliferation. This report describes the results of the investigation, related to decay heat removal, core/fuel-assembly thermal-hydraulics and thermal-hydraulic correlations, that was performed in fiscal l999 as a part of the feasibility study. ln the study of the decay heat removal, the effects of several design parameters on the performance of the reactor vessel auxiliary cooling system (RVACS) in a middle-scale sodium-cooled FR were clarified by using a plant dynamic analysis code. The upper limit of RVACS performance was preliminarily estimated at approximately 0.5 0.6 MWe. Numerical methods for the plant dynamic analysis of gas-and heavy-metal-cooled FRs were also developed. They were applied to the preliminary calculations of the transition from scram to natural circulation and the transient characteristics in tentative plant design concepts were clarified. ln addition, a dimensionless number indicating natural circulation performance was deduced for the comparison of several plant design concepts. With respect to the core/fuel-assembly thermal-hydraulics, numerical analysis methods were improved for the pin-type fuel assembly of gas-and heavy-metal-cooled FRs, the coated-particle- type fuel assembly of helium-gas-cooled FR, and the ductless core of sodium-and heavy-metal-cooled FRs. As preliminary evaluations, thermal-hydraulics in the heavy-metal-cooled FR fuel assembly was compared with sodium-cooled one and thermal-hydraulic analyses of carbon-dioxide- and helium-gas-cooled FR fuel assemblies were performed. The analysis for the fuel assembly with inside duct of sodium-cooled FR was also carried out. The correlations of pressure loss and heat transfer coefficient were investigated for the thermal-hydraulic ...
0.6 MWe. Numerical methods for the plant dynamic analysis of gas-and heavy-metal-cooled FRs were also developed. They were applied to the preliminary calculations of the transition from scram to natural circulation and the transient characteristics in tentative plant design concepts were clarified. ln addition, a dimensionless number indicating natural circulation performance was deduced for the comparison of several plant design concepts. With respect to the core/fuel-assembly thermal-hydraulics, numerical analysis methods were improved for the pin-type fuel assembly of gas-and heavy-metal-cooled FRs, the coated-particle- type fuel assembly of helium-gas-cooled FR, and the ductless core of sodium-and heavy-metal-cooled FRs. As preliminary evaluations, thermal-hydraulics in the heavy-metal-cooled FR fuel assembly was compared with sodium-cooled one and thermal-hydraulic analyses of carbon-dioxide- and helium-gas-cooled FR fuel assemblies were performed. The analysis for the fuel assembly with inside duct of sodium-cooled FR was also carried out. The correlations of pressure loss and heat transfer coefficient were investigated for the thermal-hydraulic ...
Takeda, Toshikazu*; *; Kitada, Takanori*; *
PNC TJ9605 97-001, 100 Pages, 1997/03
This report is composed of the following two parts and appendix. (I)Improvement of the Method for Evaluating Reactivity Based on Monte Carlo Perturbation Theory (II)Improvement of Nodal Transport Method for 3-D Hexagonal Geometry (Appendix) Effective Cross Section of  U Samples for Analyzing Doppler Reactivity in Fast Reactors Part I. Improvement of the Method for Evaluating Reactivity Bascd on Monte Carlo Perturbation Theory. Theoretical formulation in Monte Carlo perturbation method had been checked, and then introduced into a calculation code. The increase of CPU time is about 10 to 20 % compared to that if normal Monte Carlo code, in the cases of same number of history. This Monte Carlo perturbation method found to be effective, because results are almost reasonable and deviations of the results are especially small, by using the Monte Carlo perturbation code. However, there are somc cases that the results of the change of eigenvalues becomes positive or negative by changing the estimator, and there is no reasonable difference in the results between the conventional method, which does not consider the change of neutron source distribution caused by a perturbation, and the new method, which consider that change. Thus it is still necessary to check the Monte Carlo pcrturbation code. Part II. Improvement of Nodal Transport Method for 3-D Hexagonal Geometry It is certain that we can accurately evaluate hexagonal geometry FBR core by nodal transport calculation code for hexagonal-Z geometry named 'NSHEX'. However it is also found that in very heterogeneous core the results is not good enough. Because the treatment of the transverse leakage to the radial direction, which is use for evaluating intra-nodal flux distribution, is not so accurate. For the treatment of the leakage distribution, it is necessary to estimate the nodal vertex flux. In conventional method, the vertex flux estimated by the surrounding node surfacc flux around that vertex. On the contrary,
U Samples for Analyzing Doppler Reactivity in Fast Reactors Part I. Improvement of the Method for Evaluating Reactivity Bascd on Monte Carlo Perturbation Theory. Theoretical formulation in Monte Carlo perturbation method had been checked, and then introduced into a calculation code. The increase of CPU time is about 10 to 20 % compared to that if normal Monte Carlo code, in the cases of same number of history. This Monte Carlo perturbation method found to be effective, because results are almost reasonable and deviations of the results are especially small, by using the Monte Carlo perturbation code. However, there are somc cases that the results of the change of eigenvalues becomes positive or negative by changing the estimator, and there is no reasonable difference in the results between the conventional method, which does not consider the change of neutron source distribution caused by a perturbation, and the new method, which consider that change. Thus it is still necessary to check the Monte Carlo pcrturbation code. Part II. Improvement of Nodal Transport Method for 3-D Hexagonal Geometry It is certain that we can accurately evaluate hexagonal geometry FBR core by nodal transport calculation code for hexagonal-Z geometry named 'NSHEX'. However it is also found that in very heterogeneous core the results is not good enough. Because the treatment of the transverse leakage to the radial direction, which is use for evaluating intra-nodal flux distribution, is not so accurate. For the treatment of the leakage distribution, it is necessary to estimate the nodal vertex flux. In conventional method, the vertex flux estimated by the surrounding node surfacc flux around that vertex. On the contrary,
;
PNC TN9410 97-013, 111 Pages, 1997/01
Since the 54-rod cluster high-burnup fuel assemblies are planing to be loaded in Fugen, it must be confirmed that the mechanical integrity of the assemblies will be retained during the dwelling period in the reactor core. In the integrity verification, the confirmation that fretting wear, which occurs on fuel cladding surface at the contact with the spacer ring-elements, will not exceed the design margin is important. Accurate measurements of the flow-induced vibration characteristics under the hydraulic condition of coolant simulating the reactor core, especially measurements of the vibration amplitude, is necessary because the vibration amplitude directly affects the fretting wear depth. The flow-induced vibration measurements of the 54-rod cluster high-burnup fuels in which accelerometers were installed, were carried out under the various hydraulic conditions in the Component-Test-Loop (CTL). The results of the measurements are discribed in this papers. From the frequency analysis, the characteristic frequency of the fuel was observed around 105 Hz and 160 Hz. This frequency approximately coincided with that estimated by the fretting wear analysis code. The amplitude of flow-induced vibration was increased with increase in total flow rate and steam quality. Though these tendencies coincided with the results calculated by the analysis code, the amplitude measured at the region of low flow rate tended to be large compared with the calculated values. It was confirmed that this difference can be reduced on the safety side by the modification of the equation in the analysis code. The Paidoussis equation is divided into two terms in this modification, in which one term depending on total flow rate and the other term depending on steam quality, and proper coefficients are determined for each term. Though the amplitudes of flow-induced vibration for this fuel were larger than for either of the 28-rod cluster fuel of Fugen and 36-rod cluster fuel of ATR demonstration ...
Mori, Tomoaki
PNC TN9410 96-293, 101 Pages, 1996/11
In criticality Engineering Section, experiments for sub-criticality measurements by use with DCA (Deuterium Critical Assmbly) two-region core loaded with the test fuel assembly using MK-I fuels of JOYO are planed for the purpose of performing the study of sub-criticality measurements, Through this report, nuclear characteristics of DCA two-region core loaded with MK-I test fuels bave been understood with the satisfaction of DCA nuclear limits. And also, the composition of test fuel assembly in DCA core was decided from these results. SCALE4.2 code system including KENO-V with multi-group monte carlo method was used in order to calculate these nuclear characteristics. The estimated items of nuclear characteristics are critical heavy water height, heavy water level reactivity coefficient, heavy water dump reactivity and safety rod reactivity worth.
Ohtaki, Akira;
PNC TN9410 96-142, 102 Pages, 1996/04
In order to evaluate the pressure history at the leaked position and the amount of sodium leakage regarding the sodium leak accident of MONJU, the plant system dynamics were calculated by Super-COPD. It was estimated from the calculated results that the sodium leakage was halted around 23:28, which was 3 hours and 41 minutes after the initiation. The pressure loss coefficient of the leaked position was evaluated to be 2.16 in two kinds of the water experiments of PNC and of Toshiba-IHI. Using cofficient to the calculated pressure history, the minimum and the maximum leakage rates were evaluated to be 35.5 and 51.9g/sec respectively, and the average rate was 48.9g/sec. Therefore, the total amount of sodium leakage was estimated to be 650 38kg.
38kg.
*; *; *; Sato, Wakaei*; *; Sanda, Toshio*
PNC TN9410 95-214, 199 Pages, 1995/08
In order to improve the design method and accuracy of large fast breeder cores, extensive work has been performed to accumulate and evaluate many kinds of results of fast reactor physics experiments and analyses. As a part of efforts to develop a standard data base for LMFBR core nuclear design, the present report evaluates the physical consistency of JUPITER experimental analysis, especially concentrating on criticality. Here, the judgment of consistency is based on not only the deviation degree of C/E values from unity, but also various viewpoints such as the comparison with other cores or other nuclear characteristics by sensitivity analysis, the effect of changing nuclear data library, the analysis of FCA and JOYO which have completely different source of data from JUPITER, and the use of the Monte Carlo method as an analytical reference. (1)The C/E values of JUPITER criticality are slightly underestimated in the range of 0.993-0.999, using the JFS-3-J2 (1989) group constant set based on JENDL-2 and three-dimensional XYZ transport theory with the most detailed analytical model. There is an obvious dependency of C/Es on reactor core concepts with homogeneous or heterogeneous structure, the main cause of which is considered to be the effect of internal blanket existence and cross-section errors of JFS-3-J2, judged from sensitivity analysis. (2)The latest analytical method and model based on three-dimensional XYZ transport theory has sufficient ability to predict the relative changes of JUPITER criticality caused by the effect of reactor core size, CRP sodium channel, control rod and internal blankets. (3)The analytical error of JUPITER criticality was evaluated as approximately 0.3%dk and this seems reasonable, because the results of Monte Carlo analysis for ZPPR-9 criticality were almost identical with those of our standard analytical method. (4)The analytical results based on the latest JENDL-3.2 library were very close to those of JENDL-2 results, ...
Obara, Toru*; Horiki, Oichiro*; Nakajima, Teruo; Watanabe, Shukichi; Ishijima, Kiyomi; Katanishi, Shoji
JAERI-Review 95-010, 39 Pages, 1995/06
no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Koji; Shimazaki, Junya; Nabeshima, Kunihiko; Shinohara, Yoshikuni; Inoue, Kimio*;
JAERI-Research 95-004, 178 Pages, 1995/01
no abstracts in English
Nakagiri, Toshio; ; Ohno, Shuji; ; *; Koyama, Shinichi; Shimoyama, Kazuhito
PNC TN9510 94-001, 246 Pages, 1994/05
None
; Yamaguchi, Akira
PNC TN9410 93-213, 28 Pages, 1993/10
Loop-version of Super System Code (SSC-L) has been applied to the analysis of the secondary loop natural circulation test (heated up by the pumps: 4.3MWt) in Monju. The purposes of this study are to validate the computer program and to point out the additional plant data necessary for the analysis of the proposed tests with better accuracy. From the test results, generated heat in the pumps is 4.3 MWt while the removed heat at ACS is 3.4 MWt in the initial steady state. The difference is caused by heat losses from the heat transport system and it is taken into account in the SSC model. The tansient thermohydraulic performance in the secondary heat tansport system simulated using SSC-L is in agreement with the test data. Hence, the pressure loss model in SSC-L is validated and the code is applicable to the natural circulation conditions. Validation of other component models in SSC-L is in progress using Monju data towards a whole plant natural circulation test.
Hayashi, Koji; Shimazaki, Junya; Nabeshima, Kunihiko; Shinohara, Yoshikuni; Inoue, Kimio*;
JAERI-M 93-194, 163 Pages, 1993/10
no abstracts in English
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki;
PNC TN9410 92-371, 94 Pages, 1992/12
TRU nuclides (Np, Am, and Cm) contained in the high level waste have extremely long-term radioactivity. They would be managed much more easily if transmuted in a short period. The present study deals with TRU transmutation by Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs). The results are summarized below. (1)Study on a 300MWe Super Long Life Core for TRU Transmutation An FBR core loaded with TRU has a large potentiality of extending operation cycle length. Making use of the potentiality, a super long life FBR core loaded with TRU was studied aiming at continuous operation without refueling during plant life and efficient reduction of TRU nuclides. Core parameters were optimized with the electric power of 300MWe and analyses of nuclear and thermal characteristics were carried out. As a result, the burnup reactivity change of the optimized core for 34 years is very small (2.5%  k/kk'). The power swing is also small, which resulted in satisfaction of the thermal design criteria. The amount of TRU transmuted during lifetime is about 5300Kg, which is equal to that 6 LWRs of 1000MWe produce during their lifetime. The Doppler coefficient (absolute value) is rather small because of TRU loading. Further study is needed on core kinetics from the view point of core safety and control. (2)Study on influence of uncertainties of TRU cross sections There are large uncertainties in TRU cross sections because of lack of experimental data. The influences of the uncertainties upon nuclear characteristics were evaluated for the super long life core and a large FBR core loaded with TRU of 5%. Sensitivity analysis on cross sections was carried out and uncertainties of nuclear characteristics were roughly evaluated. Based on the results, the TRU cross sections with large influences were identified.
k/kk'). The power swing is also small, which resulted in satisfaction of the thermal design criteria. The amount of TRU transmuted during lifetime is about 5300Kg, which is equal to that 6 LWRs of 1000MWe produce during their lifetime. The Doppler coefficient (absolute value) is rather small because of TRU loading. Further study is needed on core kinetics from the view point of core safety and control. (2)Study on influence of uncertainties of TRU cross sections There are large uncertainties in TRU cross sections because of lack of experimental data. The influences of the uncertainties upon nuclear characteristics were evaluated for the super long life core and a large FBR core loaded with TRU of 5%. Sensitivity analysis on cross sections was carried out and uncertainties of nuclear characteristics were roughly evaluated. Based on the results, the TRU cross sections with large influences were identified.